What is the Flow Coefficient
The Flow Coefficient, known as Cv (US/EU Standard), Kv (International Standard), or C-value, is a critical technical parameter defining the flow capacity of industrial valves like control valves and regulators.
Defining Cv Value
Valve Cv represents the flow coefficient indicating a valve’s capacity to pass fluid under specific conditions. It quantifies the volume flow rate of liquid or gas through a valve at a given pressure drop. Higher Cv values indicate greater flow capacity.
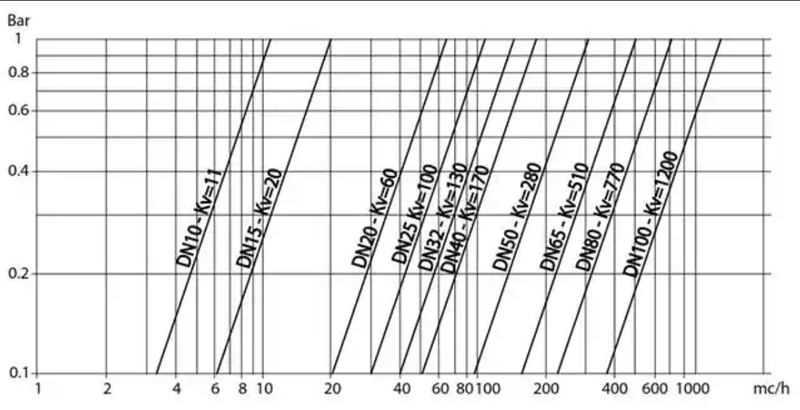
What is Cv (Capacity Value)
Valve Cv (Capacity Value) measures flow capacity and is calculated under standardized test conditions:
• Valve fully open
• Pressure drop (ΔP) of 1 psi across the valve
• Fluid: Water at 60°F (15.5°C)
• Flow rate: US gallons per minute (GPM)
Valve Opening vs. Cv Value
Cv/Kv and valve opening (%) are distinct concepts:
• Kv Definition (China Standard): Flow rate in m³/h when ΔP = 100 kPa, fluid density = 1 g/cm³ (water at room temperature).
*Example: Kv=50 means 50 m³/h flow at 100 kPa ΔP.*
• Opening Percentage: Position of valve plug/disc (0% = closed, 100% = fully open).
Calculating Cv & Key Applications
Cv is influenced by valve design, size, material, flow regime, and fluid properties (temperature, pressure, viscosity).
The core formula is:
Cv = Q / (√ΔP × √ρ)
Where:
• Q = Volumetric flow rate
• ΔP = Pressure differential
• ρ = Fluid density
Conversion: Cv = 1.167 Kv
Role in Valve Selection & Design
Cv directly impacts fluid control system efficiency:
• Determines optimal valve size and type for target flow rates
• Ensures system stability (e.g., prevents pump cycling in building water supply)
• Critical for energy optimization
Cv Variations Across Valve Types
Flow capacity differs by valve design (data sourced from ASME/API/ISO standards):
| Valve Type | Key Characteristics | Example Cv (FCI Standard) |
|---|---|---|
Gate Valve |
Medium Cv (DN100 ≈ 400); poor regulation; avoid <30% opening (turbulence risk per ASME B16.34) | DN50: ~120 |
Ball Valve |
High Cv (1.8× gate valves); linear flow control; API 6D recommended for pipelines | DN80 V-ball: ≈375 |
Butterfly Valve |
Cost-effective for large sizes; ±5% precision (triple-offset); limited flow gain >70% open | DN150 Wafer: ~2000 |
Globe Valve |
High resistance (Cv ≈ 1/3 of ball valves); precise control (medical/lab use) | DN50: ~40 |
Core Flow Parameters & Influencing Factors
Valve performance is defined by three parameters (per Fluid Controls Institute):
1. Cv Value: GPM flow at 1 psi ΔP (e.g., DN50 ball valve ≈ 210 vs. gate valve ≈ 120).
2. Flow Resistance Coefficient (ξ):
• Butterfly valve: ξ = 0.2–0.6
• Globe valve: ξ = 3–5
Selection Guidelines & Critical Considerations
Viscosity Correction:
Apply multipliers to Cv (e.g., crude oil: 0.7–0.9 per ISO 5208).
Smart Valves:
Real-time Cv optimization (e.g., Emerson DVC6200 positioner).
Flow Coefficient Testing Systems
Testing requires controlled conditions due to measurement sensitivity:
• Setup (Per Fig. 1):
Flowmeter, thermometer, throttling valves, test valve, ΔP gauge.
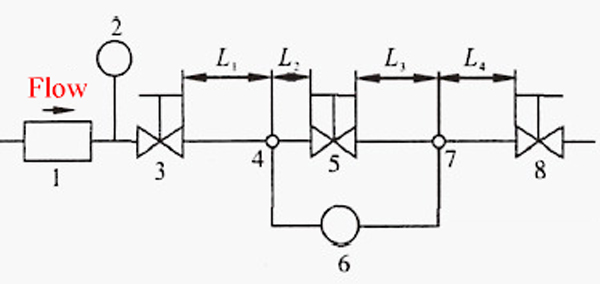
1. Flow meter 2. Thermometer 3. Upstream throttle valve 4 and 7. Pressure tapping holes 5. Test valve 6. Pressure differential measuring device 8. Downstream throttle valve
4. The distance between the pressure tapping hole and the valve is 2 times the pipe diameter
7. The distance between the pressure tapping hole and the valve is 6 times the pipe diameter
• Key Controls:
- Upstream valve regulates inlet pressure.
- Downstream valve maintains stable pressure (nominal size > test valve to ensure choked flow occurs in test valve).
• Standards:
JB/T 5296-91 (China) vs. BS EN1267-1999 (EU).
• Critical Factors:
Tap location, piping configuration, Reynolds number (liquids), Mach number (gases).
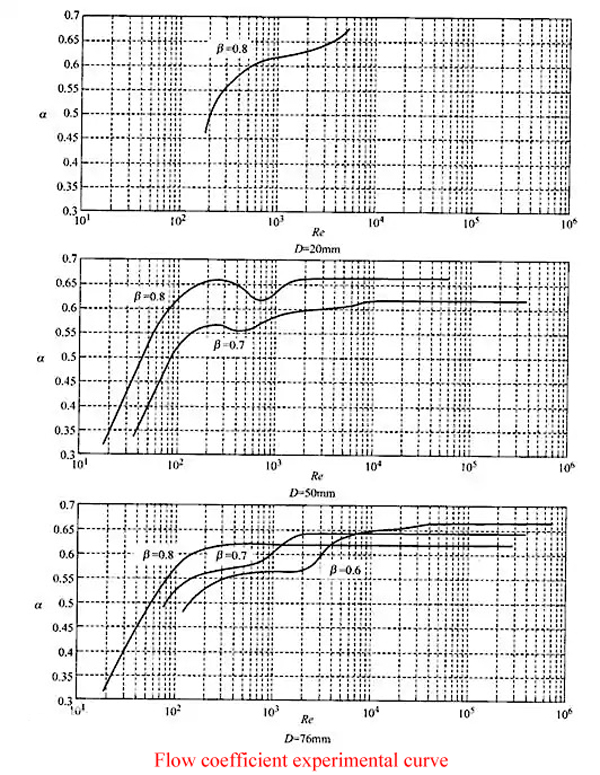
Testing Limitations & Solutions:
• Current systems test valves ≤DN600.
• Larger valves: Use air-flow testing (not detailed here).
Impact of Reynolds Number: Experimental data confirms Reynolds number significantly affects test results.
Key Takeaways
• Cv/Kv defines valve flow capacity under standardized conditions.
• Valve type, size, and fluid properties critically impact Cv.
• Testing requires strict adherence to protocols (JB/T 5296-91/BS EN1267) for accuracy.
• Corrections apply for viscosity, temperature, and pressure.
(All data sourced from ASME/API/ISO standards and valves manufacturer whitepapers.)
Post time: Jan-06-2025






