Different type valves are control components in fluid delivery systems, mainly used to open and close pipelines, control flow direction, and regulate and control parameters of the delivery medium (such as temperature, pressure, and flow).
Mainly 8 Types of Valves for market and Pipeline
Ball Valves
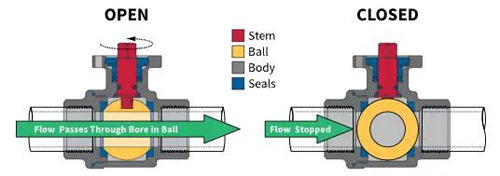
A ball valve has the smallest fluid resistance among all valve types, and even the reduced diameter ball valve has a fairly small fluid resistance. The opening and closing part of the ball valve is a sphere with a hole, which rotates around an axis perpendicular to the channel to achieve the purpose of opening and closing the channel.
Quarter-turn Two-way Ball Valves are by far the most common type of process control valve. They are two-way (inlet and outlet), two-position (open and closed) valves used to close or isolate systems, circuits or components within the system.
Plug Valves
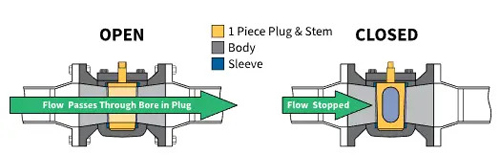
The valve plug of the plug valve is usually cylindrical or conical, and the channel shape can be rectangular or trapezoidal as needed. This valve has a simple structure, fast switching, low fluid resistance, and is easy to adapt to multi-channel structures.
Plug valves are usually used to cut off and connect media, as well as to divert flow, but can also be used for throttling. Since the plug body of the plug valve rotates with the valve stem to achieve the opening and closing action, it can also be used for media with suspended particles.
Butterfly Valve
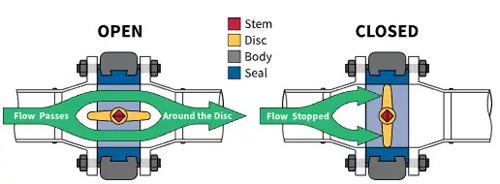
The butterfly valve is a common flow control valve. Its working principle is to control the flow of the fluid by adjusting the position of the butterfly. When the butterfly rotates, the fluid changes its position through the butterfly, thereby changing the size of the flow.
The valve disc rotates 90° within the range of the valve seat to achieve the opening and closing of the valve.
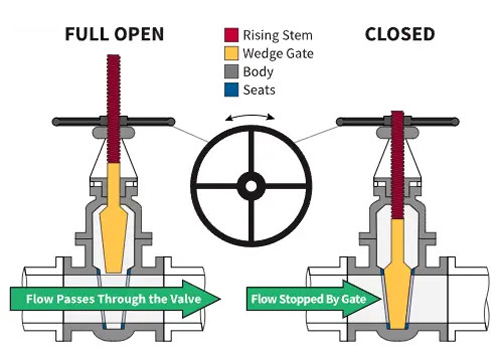
Gate Valve
The opening and closing part of a gate valve is the gate. The movement direction of the gate is perpendicular to the direction of the fluid. The gate valve can only be fully opened and fully closed, and cannot be adjusted or throttled.
The gate has two sealing surfaces. The two sealing surfaces of the most commonly used mode gate valve form a wedge shape, and the wedge angle varies with the valve parameters.
Globe Valve
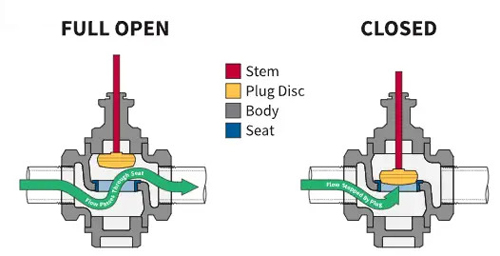
The working principle of the globe valve is to rely on the valve stem pressure to make the valve disc sealing surface fit closely with the valve seat sealing surface to prevent the flow of the medium. When the valve is closed, pressure must be applied to the disc to force the sealing surface to not leak.
Globe valves are suitable for both on/off and throttling applications. Two-way globe valves are preferred for precise flow control, and three-way globe valves are often used to mix media from two inlets and direct the mixture through the outlet.
Needle Valves
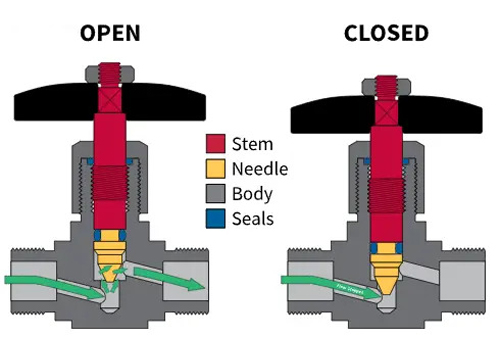
These valves are very similar to globe valves, but have two main differences. First, they are smaller, which can better control flow on smaller lines. Second, they use a conical “needle” instead of a disc-shaped plug and an orifice needle valve for precise flow control.
Solenoid Valves
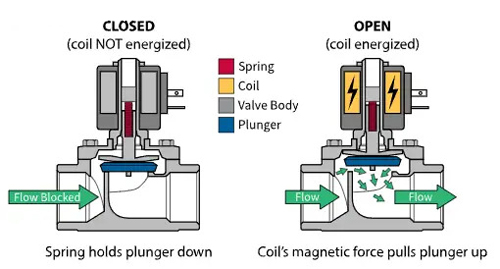
Solenoid valves work by passing an electric current through a coil, which causes the coil to generate a magnetic field, which acts on the iron core to generate magnetic attraction, and the iron core moves toward the coil, causing the valve to open.
Solenoid valves are relatively small. Their size is limited by the strength of the coil, which is the result of the winding used to generate the magnetic field when energized. In addition to the limitation of coil strength, the flow path and orifice in the solenoid valve are also quite small compared to the size of the pipeline.
Angle Piston Valve
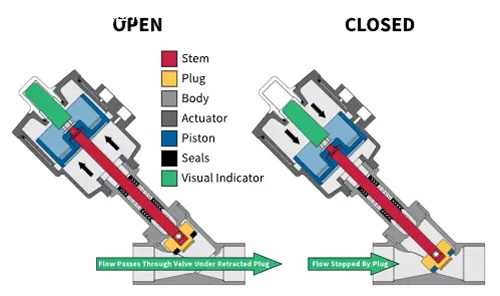
An angle piston valve is a special type of valve that has a built-in pneumatic actuator and is usually classified as a two-position valve. The actuator can be spring return or double acting, depending on the application requirements.
The key component in the valve is the valve plug, which is placed in the flow channel at a certain angle and sits in an inclined valve seat molded into the valve flow path.
When the valve is open, the valve plug is almost completely retracted out of the flow channel. This design allows the angle piston valve to have a large flow rate and low pressure drop, making it a fast-acting valve. In many on/off applications, angle seat valves are a cost-effective choice that can replace traditional ball valves.
Summary
There are many types of valves, and the valve design varies according to different working conditions and usage requirements. In addition to the 8 commonly used valves mentioned above, there are many other types of valves, such as plug valves, regulating valves, shut-off valves, HIPPS valves, etc.
When choosing a valve, you can consult a World-renowned Valve Supplier or a Chinese Valve Factory.
Post time: Feb-22-2025