What is a DBB Plug Valve
DBB Plug Valve is a double block and bleed plug valve: a single-piece valve with two seat sealing surfaces, when it is in the closed position, it can block the medium pressure from the upstream and downstream ends of the valve at the same time, and is clamped between the seat sealing surfaces The valve body cavity medium has a relief channel.
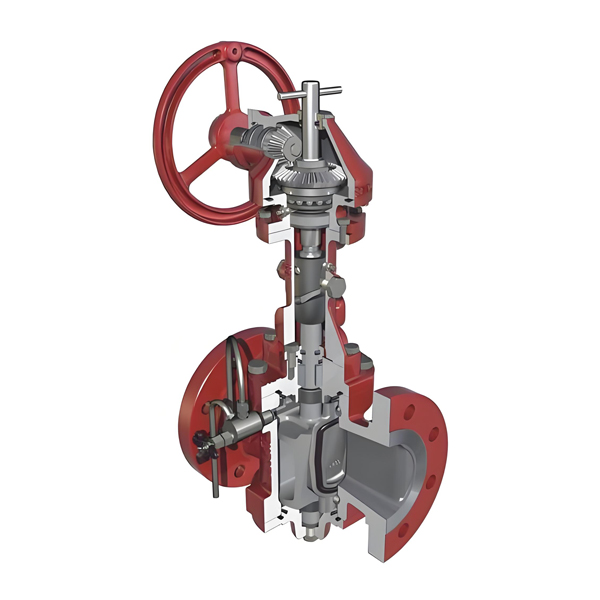
The working principle of DBB plug valve
1. Structure of DBB plug valve
The structure of DBB plug valve is divided into five parts: upper bonnet, plug, sealing ring seat, valve body and lower bonnet.
- The plug body of the DBB plug valve is composed of a conical valve plug and two valve discs to form a cylindrical plug body. The valve discs on both sides are inlaid with rubber sealing surfaces, and the middle is a conical wedge plug.
- When the valve is opened, the transmission mechanism makes the valve plug rise, and drives the valve discs on both sides to close, so that the valve disc seal and the valve body sealing surface are separated, and then drives the plug body to rotate 90° to the fully open position of the valve.
- When the valve is closed, the transmission mechanism rotates the valve plug 90° to the closed position, and then pushes the valve plug to descend, the valve discs on both sides contact the bottom of the valve body and no longer move down, the middle valve plug continues to descend, and the two sides of the valve are pushed by the inclined plane. The disc moves to the sealing surface of the valve body, so that the soft sealing surface of the disc and the sealing surface of the valve body are compressed to achieve sealing. The friction action can ensure the service life of the valve disc seal.
2. The advantages of DBB plug valve
DBB plug valves have extremely high sealing integrity. Through the unique wedge-shaped cock, L-shaped track and special operator design, the valve disc seal and the valve body sealing surface are separated from each other during the operation of the valve, thus avoiding the generation of friction, eliminating the seal wear and prolonging the valve life. The service life improves the reliability of the valve. At the same time, the standard configuration of the thermal relief system ensures the safety and ease of operation of the valve with absolute shut-off, and at the same time provides on-line verification of the tight shut-off of the valve.
Six characteristics of DBB plug valve
1. The valve is an active sealing valve, which adopts a conical cock design, does not rely on the pressure of the pipeline medium and the spring pre-tightening force, adopts a double-sealing structure, and forms an independent zero-leakage seal for the upstream and downstream, and the valve has high reliability.
2. The unique design of the operator and L-shaped guide rail completely separates the valve disc seal from the valve body sealing surface during valve operation, eliminating seal wear. The valve operating torque is small, suitable for frequent operation occasions, and the valve has a long service life.
3. Online maintenance of the valve is simple and easy. The DBB valve is simple in structure and can be repaired without removing it from the line. The bottom cover can be removed to remove the slide from the bottom, or the valve cover can be removed to remove the slide from the top. The DBB valve is relatively small in size, light in weight, convenient for disassembly and maintenance, convenient and fast, and does not require large lifting equipment.
4. The standard thermal relief system of the DBB plug valve automatically releases the valve cavity pressure when overpressure occurs, enabling real-time online inspection and verification of valve sealing.
5. Real-time indication of valve position, and the indicator needle on the valve stem can feedback the real-time status of the valve.
6. The bottom sewage outlet can discharge impurities, and can discharge the water in the valve cavity in winter to prevent the valve body from being damaged due to volume expansion when the water freezes.
3. Failure analysis of DBB plug valve
1. The guide pin is broken. The guide pin is fixed on the valve stem bearing bracket, and the other end is sleeved on the L-shaped guide groove on the valve stem sleeve. When the valve stem switches on and off under the action of the actuator, the guide pin is restricted by the guide groove, so the valve is formed. When the valve is opened, the plug is lifted up and then rotated by 90°, and when the valve is closed, it is rotated by 90° and then pressed down.
The action of the valve stem under the action of the guide pin can be decomposed into horizontal rotation action and vertical up and down action. When the valve is opened, the valve stem drives the L-shaped groove to rise vertically until the guide pin reaches the turning position of the L-shaped groove, the vertical speed decelerates to 0, and the horizontal direction accelerates the rotation; when the valve is closed, the valve stem drives the L-shaped groove to rotate in the horizontal direction to When the guide pin reaches the turning position of the L-shaped groove, the horizontal deceleration becomes 0, and the vertical direction accelerates and presses down. Therefore, the guide pin is subjected to the greatest force when the L-shaped groove turns, and it is also the easiest to receive the impact force in the horizontal and vertical directions at the same time. Broken guide pins.
After the guide pin is broken, the valve is in a state where the valve plug has been lifted but the valve plug has not been rotated, and the diameter of the valve plug is perpendicular to the diameter of the valve body. The gap passes but fails to reach the fully open position. From the circulation of the passing medium, it can be judged whether the valve guide pin is broken. Another way of judging the breakage of the guide pin is to observe whether the indicator pin fixed at the end of the valve stem is open when the valve is switched. Rotation action.
2. Impurity deposition. Since there is a large gap between the valve plug and the valve cavity and the depth of the valve cavity in the vertical direction is lower than that of the pipeline, impurities are deposited on the bottom of the valve cavity when the fluid passes through. When the valve is closed, the valve plug is pressed down, and the deposited impurities are removed by the valve plug. It is flattened at the bottom of the valve cavity, and after several depositions and then flattened, a layer of “sedimentary rock” impurity layer is formed. When the thickness of the impurity layer exceeds the gap between the valve plug and the valve seat and can no longer be compressed, it will hinder the stroke of the valve plug. The action causes the valve to not close properly or to over-torque.
3. Internal leakage of the valve. The internal leakage of the valve is the fatal injury of the shut-off valve. The more internal leakage, the lower the reliability of the valve. The internal leakage of the oil switching valve may cause serious oil quality accidents, so the selection of the oil switching valve needs to be considered. The internal leakage detection function of the valve and the difficulty of internal leakage treatment. The DBB plug valve has a simple and easy-to-operate internal leakage detection function and internal leakage treatment method, and the double-sided sealing valve structure of the DBB plug valve enables it to have a reliable cut-off function, so the oil product switching valve of the refined oil pipeline mostly uses the DBB plug.
DBB plug valve internal leakage detection method: open the valve thermal relief valve, if some medium flows out, it stops flowing out, which proves that the valve has no internal leakage, and the outflow medium is the pressure relief existing in the valve plug cavity; if there is continuous medium outflow, It is proved that the valve has internal leakage, but it is impossible to detect which side of the valve is internal leakage. Only by disassembling the valve can we know the specific situation of the internal leakage. The internal leakage detection method of the DBB valve can realize on-site rapid detection, and can detect the internal leakage of the valve when switching between different oil product processes, so as to prevent oil product quality accidents.
4. Dismantling and inspection of DBB plug valve
Inspection and maintenance include online inspection and offline inspection. During online maintenance, the valve body and flange are kept on the pipeline, and the purpose of maintenance is achieved by disassembling the valve components.
The disassembly and inspection of the DBB plug valve is divided into the upper disassembly method and the lower disassembly method. The upper disassembly method is mainly aimed at the problems existing in the upper part of the valve body such as the valve stem, the upper cover plate, the actuator, and the valve plug. The dismantling method is mainly aimed at the problems existing at the lower end of seals, valve discs, lower cover plates, and sewage valves.
The upward disassembly method removes the actuator, the valve stem sleeve, the sealing gland, and the upper cover of the valve body in turn, and then lifts out the valve stem and valve plug. When using the top-down method, due to the cutting and pressing of the packing seal during installation and the wear and tear of the valve stem during the valve opening and closing process, it cannot be reused. Open the valve to the open position in advance to prevent the valve plug from being easily removed when the valve discs on both sides are compressed.
The dismantling method only needs to remove the bottom lower cover to overhaul the corresponding parts. When using the dismantling method to check the valve disc, the valve cannot be placed in the fully closed position, so as to avoid the valve disc cannot be taken out when the valve is pressed. Due to the movable connection between the valve disc and the valve plug through the dovetail groove, the bottom cover cannot be removed at once when the lower cover is removed, so as to prevent the sealing surface from being damaged due to the falling of the valve disc.
The upper disassembly method and the lower disassembly method of the DBB valve do not need to move the valve body, so online maintenance can be achieved. The heat relief process is set on the valve body, so the upper disassembly method and the lower disassembly method do not need to disassemble the heat relief process, which simplifies the maintenance procedure and improves the maintenance efficiency. Dismantling and inspection does not involve the main body of the valve body, but the valve needs to be fully closed to prevent the medium from overflowing.

5. Conclusion
The fault diagnosis of DBB plug valve is predictable and periodic. Relying on its convenient internal leakage detection function, the internal leakage fault can be quickly diagnosed, and the simple and easy-to-operate inspection and maintenance operation characteristics can realize periodic maintenance. Therefore, the inspection and maintenance system of DBB plug valves has also changed from the traditional post-failure maintenance to a multi-directional inspection and maintenance system that combines pre-predictive maintenance, post-event maintenance and regular maintenance.
Post time: Jul-15-2022






