A 3 way ball valve is a versatile fluid control device widely used in industrial, commercial, and residential systems. Its unique design enables flow diversion, mixing, or shut-off in pipelines. In this article, we’ll explore the working principles, types (including stainless steel 3 way ball valves, Y type, L type, and T type), applications, and advantages of these valves.
1. Working Principle of a 3 Way Ball Valve
A 3-way ball valve consists of a hollow, rotating ball with one or two ports (holes) and three pipe connections. By rotating the ball manually or via an actuator, the flow path is redirected. Depending on the valve’s design, it can:
- Divert flow between two outlets.
- Mix fluids from two inlets into one outlet.
- Shut off flow completely.
The ball’s position determines the flow direction. For example, a 90-degree turn might switch the flow from one port to another, while a 180-degree turn could block all flow.
2. Types of 3 Way Ball Valves
Three-way ball valves are categorized based on their port configurations:
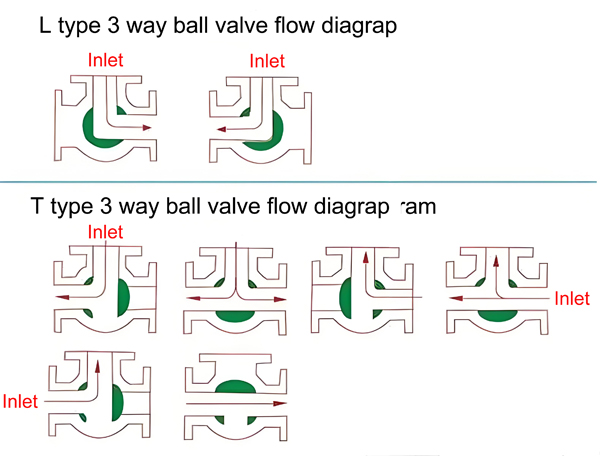
a. L-Type 3-Way Ball Valve
- The L-port valve has an “L”-shaped bore.
- It redirects flow between two ports while blocking the third.
- Applications: Ideal for flow switching (e.g., alternating between cooling and heating systems).
b. T-Type 3-Way Ball Valve
- The T-port valve features a “T”-shaped bore.
- It can mix two incoming flows or split one flow into two directions.
- Applications: Used in blending systems, such as combining hot and cold water.
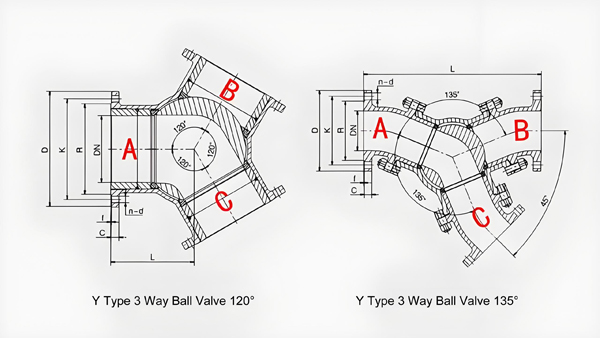
c. Y-Type 3-Way Ball Valve
- The Y-port valve has a 120-degree angled bore, minimizing pressure drop.
- Suited for applications requiring smooth flow diversion with minimal turbulence.
- Applications: Common in chemical processing and HVAC systems.
Additionally, stainless steel 3-way ball valves are popular for their corrosion resistance, making them ideal for harsh environments like marine or chemical industries.
3. Key Applications and Working Conditions
3-way ball valves are used across industries due to their adaptability:
- Industrial: Control steam, gases, or corrosive fluids in chemical plants.
- HVAC: Manage heating/cooling water distribution.
- Water Treatment: Divert or mix fluids in filtration systems.
- Oil and Gas: Handle high-pressure pipelines.
Stainless steel 3-way ball valves excel in extreme conditions, including high temperatures, corrosive media, and high-pressure systems.
4. Advantages of 3-Way Ball Valves
- Multi-Functionality: Perform mixing, diverting, and shut-off tasks with a single valve.
- Compact Design: Save space compared to using multiple 2-way valves.
- Durability: Stainless steel variants resist rust, erosion, and chemical damage.
- Low Maintenance: Simple structure with fewer leakage points.
- Quick Operation: 90-degree rotation enables fast flow control.
5. Choosing the Right 3-Way Ball Valve
Selecting the correct type depends on your system’s needs:
- Use L-type for switching between two outlets.
- Opt for T-type to mix or split flows.
- Choose Y-type for low-resistance diversion.
- For corrosive environments, prioritize stainless steel 3-way ball valves.
Conclusion
3-way ball valves are essential for efficient flow control in complex piping systems. Understanding the differences between L type, T type, and Y type valves—along with material choices like stainless steel—ensures optimal performance. Whether in industrial plants, water treatment, or HVAC systems, these valves offer reliability, versatility, and longevity.
By selecting the right configuration and material from Ball Valve Manufacturer, you can enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs in your applications.
Post time: Mar-03-2025